Beautiful Tips About How To Prevent Pleural Effusion

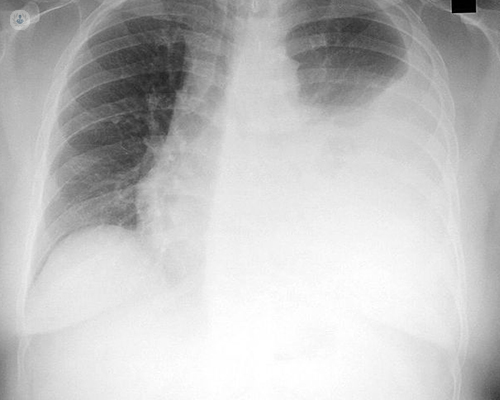
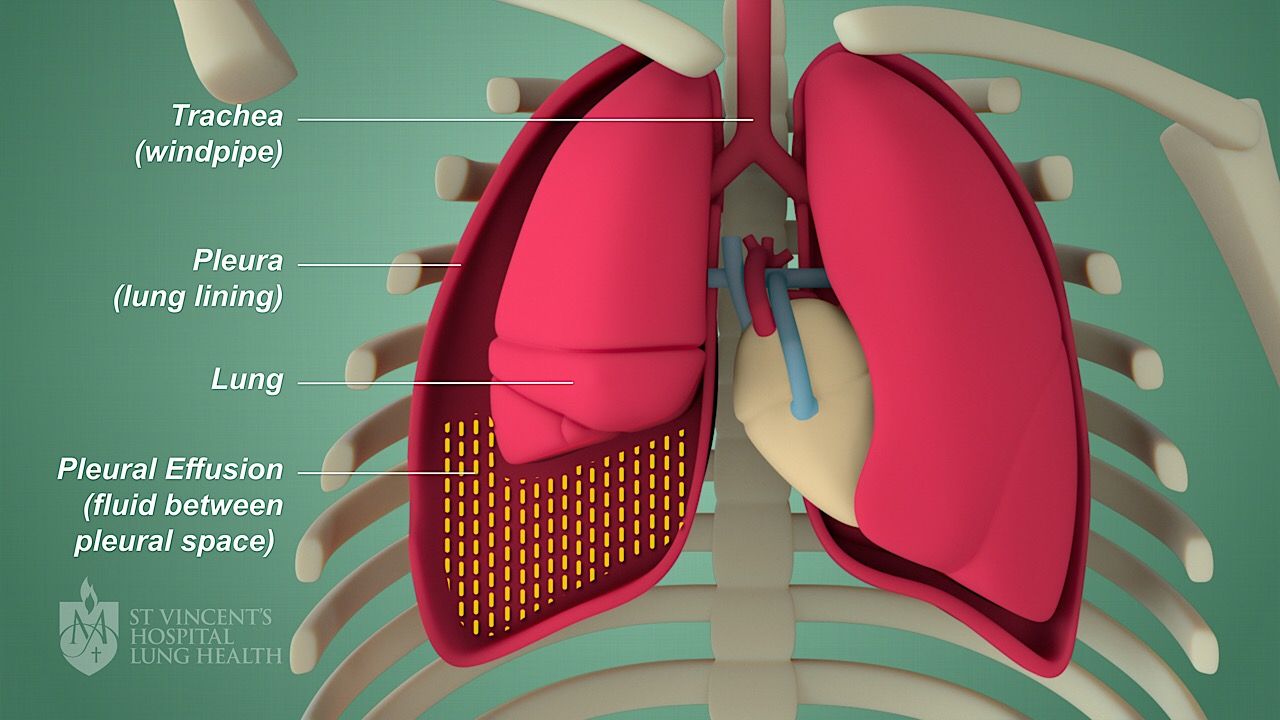
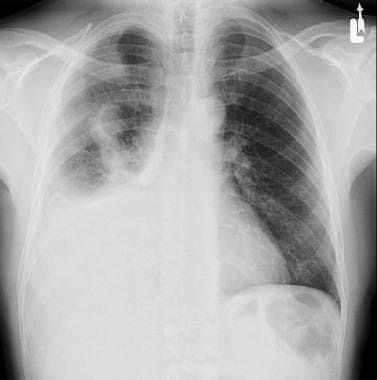
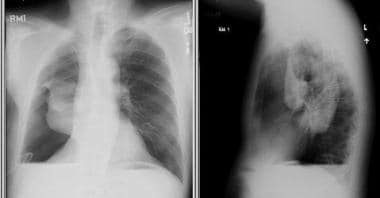
Common causes of pleural effusion include congestive heart failure, kidney failure, pulmonary embolism, trauma, or infection.
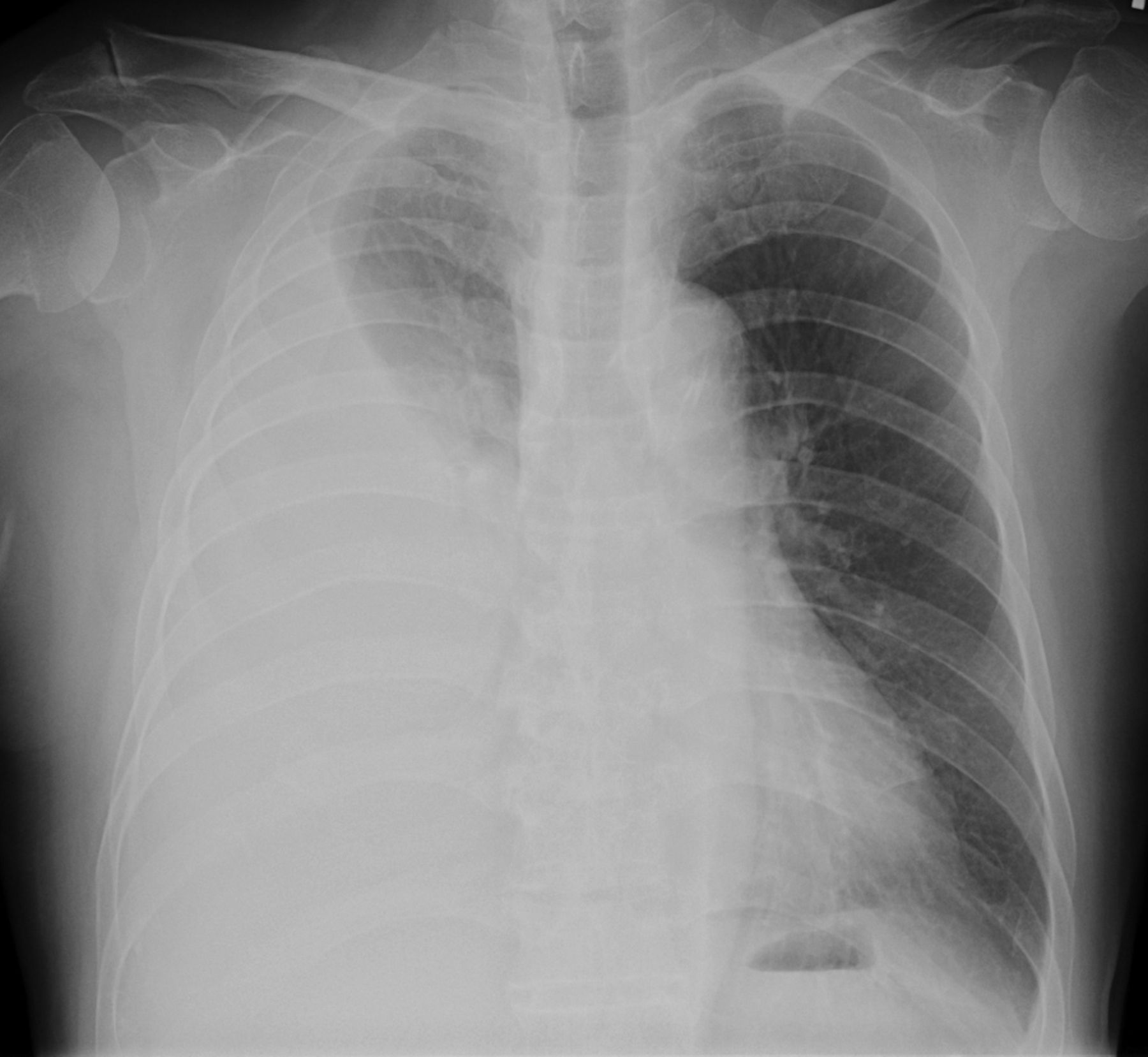
How to prevent pleural effusion. Approximately ⅔ of patients with malignant pleural effusion do not respond. The best way is to treat the cause of the effusion. Treating the cause is imperative to prevent the risk of pleural effusion recurrence.
Healthy foods include fruit, vegetables,. After removing fluid from the chest cavity, doctors administer a medication that causes the lung to stick to the chest wall, preventing future fluid buildup. Thoracotomy (also referred to as traditional, “open” thoracic surgery) a.
Eat a variety of healthy foods. Draining the pleural effusion with a needle or placing a tube in the chest to let fluid drain sealing the pleural layers to prevent more fluid from building up people who are not helped by other. Measures to prevent primary causes of pleural effusion include:
Lymphocyte predominant effusions are usually due to heart failure, malignancy, and tb. Your doctors might try to stop the fluid building up with a procedure called pleurodesis. Lean forward with your arms resting on a pillow on a bed table to allow your lungs to expand as fully as possible.
Water will thin out the fluid and you make you feel better. Anticoagulation for patients at risk of pulmonary embolism;. Treatment for a pleural effusion can be given in a hospital or an outpatient setting.
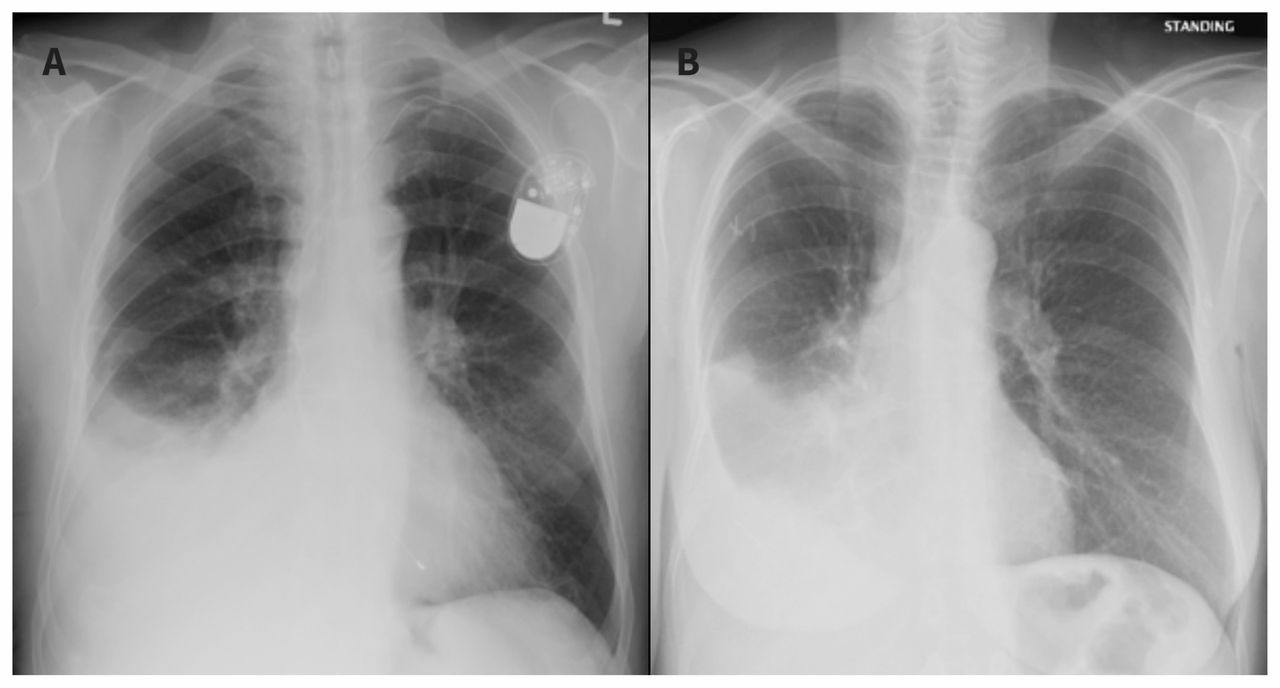
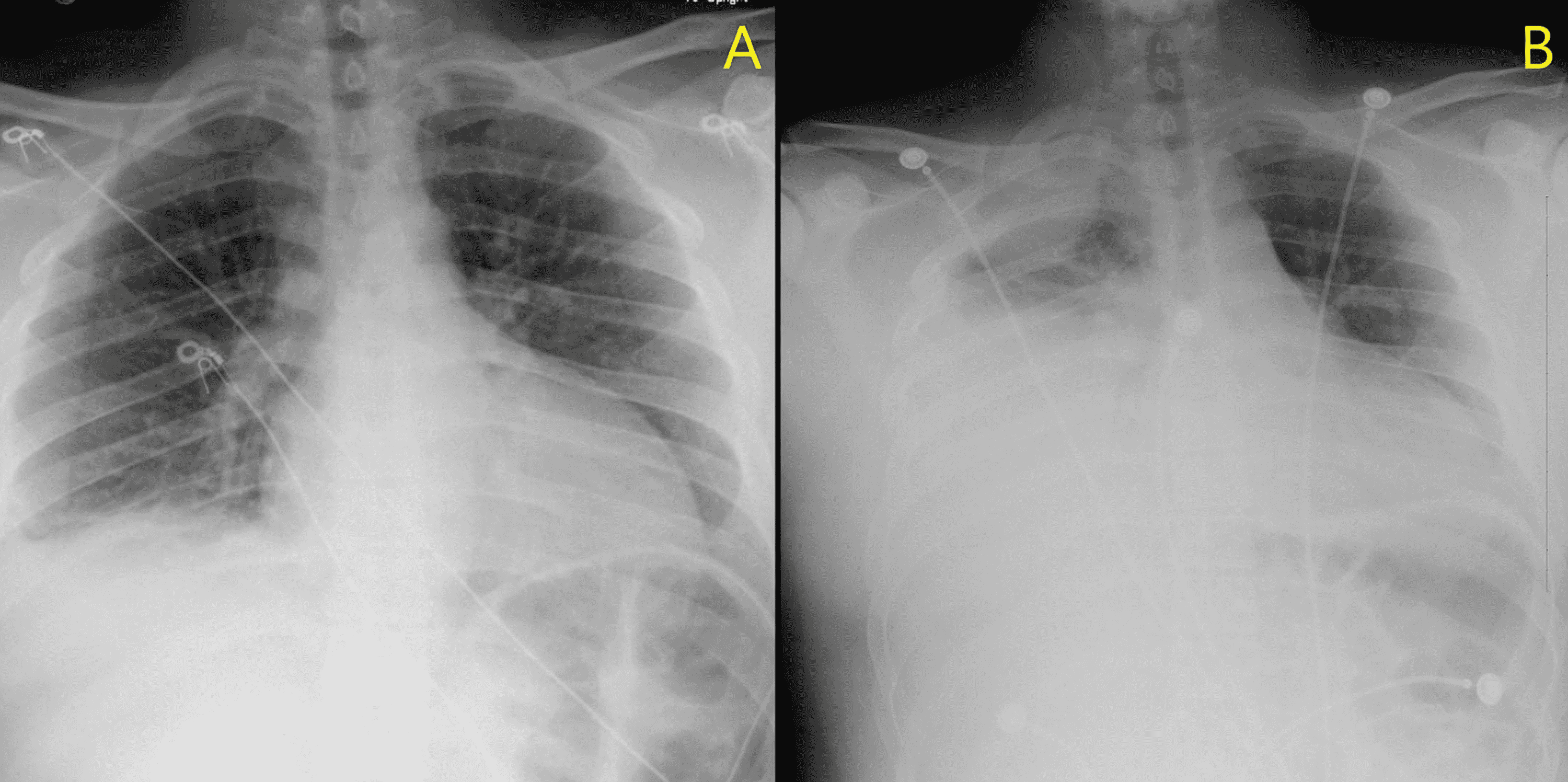
Pleural effusion how to prevent atelectsis and severe hemodynamic compromise. A very common approach is to cause inflammation and adhesions to tack the outside of the lung to the inside of the chest wall, effectively eliminating the space in which. Pleural effusions (plef) occur frequently in mechanically ventilated patients (mvp).

/malignant-pleural-effusion-2249334-5c82c9fac9e77c0001422f11.png)
/malignant-pleural-effusion-2249334-5c82c9fac9e77c0001422f11.png)